|
Towards
defined supply chain
architecture
Building
fast response, low inventory chains, is a question
of competitiveness especially in the electronics industry, where short
life
cycles emerge with high fluctuations. Also companies operating in food
business: retail, wholesale and production, are pressured by high
productivity
demand combined with fast inventory cycle requirement.
The value of lead-time is an increasingly important competitive factor
in many
industries. Management of capacity represents a way to improve
lead-times and
benefit from fast response. Traditional cost accounting methods do not
always
justify better lead-times since it may mean lower capacity utilization
and thus
higher unit costs.
Many solutions have been developed for industries related to fast
moving
consumer goods. Examples of applying the principles of agile or fast
response
supply-demand principles in the literature deal with computer
peripherals and
grocery goods. Industries with low production volume combined with high
product
mix do not have so many applications. These types of industries, such
as
machine building, construction projects, energy and infrastructure
systems, and
heavy machinery, are very important. ASDN software has a variant
analysis
functionality which allows modelling complex products and product
portfolios.
Software
approach
This
research project that developed the ASDN software addresses
how quantitative modeling techniques, such as system dynamics
simulation, may
be used for improving the purchasing and distribution logistics in
project
driven electrical utilities industries.
Complex non-linear systems including trade-off situations between may
be
represented in practical way by using computer simulation. Running
different
scenarios with a group of decision makers may improve managerial
implications.
Computer based quantitative modeling tools enable opportunities to
research new
value adding strategies for companies operating in logistics.
Additionally,
many general-purpose models may be extended to other industries and
applications of similar type.
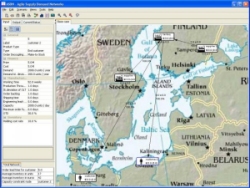
ASDN
Improves the business
As
the pilots have proven the ASDN software can help
managing global supply-demand networks to be more agile and time
responsive. The
ASDN Logistics Analysis software aims:-
- To
support modelling the characteristics of the domain: global investment
good delivery.
- To
present a rapid modeling tools for screening and presenting the
network-level controls.
- To
integrate product design with
logistics decision making
- To
suggest optimisation approaches for faster response and improved
financial performance.
Got
interested what ASDN can do for
your network? Download the Quick Guide and the software from
sourceforge.
|